Heat treatment hardening process pdf
Nitrogen Generator for Aging: Aging is a hardening process involved with precipitation of a constituent from a supersaturated solid solution. This process is typically performed on nonferrous alloys or precipitation hardening steels after rapid cooling (i.e. solution heat treatment and quenching) or …
Hardening Guide The way to the perfect knife steel This Hardening Guide contains all a knife manufacturer needs regarding the heat treatment of Sandviks knife steel. We describe, for example, what happens in the material during the hardening process itself, we compare different steel grades and suitable applications, and we provide detailed instructions for the hardening temperature that
A novel heat treatment process for surface hardening of steel has been demonstrated and named as “metal melt surface hardening (MMSH).” A surface layer with a thickness of about 400 μm and a hardness of about 700 HV has been achieved by ejecting AISI 304 stainless steel melt at a temperature
18/01/2015 · Heat treatment of steel refers to time- and temperature-controlled processes that relieve residual stresses and/or modifies material properties such as hardness (strength), ductility, and toughness. Other mechanical or chemical operations are sometimes grouped under the heading of heat treatment. The common heat-treating operations are annealing, quenching, tempering, and case hardening.
The gas nitriding process is a readily available heat treatment process that creates an extremely hard, load bearing wear resistant surface with depths ranging from .005” to .025” depth. It can be performed on many commonly available alloy steels with minimal size change and …
Heat treatment is used to modify properties of materials in addition to hardening and softening. These processes modify the behavior of the steels in a beneficial manner to
Ferritic nitrocarburising is a thermochemical surface hardening process that involves diffusion of both nitrogen and carbon into the part. Bodycote’s proprietary process of this low temperature surface treatment, called Lindure ®, involves the addition of oxygen.
Hardening of steels and cast irons represents the most popular application of induction heat treatment (Fig. 1). Induction hardening is a complex combina-tion of electromagnetic, heat transfer
Surface hardening, also known as surface heat treatment, includes transformation hardening and shock hardening. Transformation hardening is a heat-treatment process by high-power laser beam irradiation on the surface of metals and other materials. The temperature of the heated material reaches the phase transition point, but melting does not occur. After the end of the laser pulse, the metal
Due to the case hardening heat treatment process, the low-carbon steel (up to 0.25 percent carbon) produces a hard, wear-resistant surface. Medium-carbon steel The medium-carbon steels (0.25 to 0.55 % of carbon) are generally produced by through-hardening & tempering process which provides higher tensile strength ranging from 690 to 1380 MPa. Due to the lower strength of low carbon steels
Precipitation Hardening Mechanism of hardening Consider Al-Cu alloys The phase is a substitutional solid solution of copper in aluminum. whereas the intermetallic compound CuAl2 is designated the phase During the precipitation heat treatment. several transition phases are first formed in a specific sequence in relation to the development of equilibrium phase .
Work hardening or strain hardening can de described as the •The process is a heat treating process called annealing. Annealing
What is a Process (heat Treating) Atmosphere? A Mixture of Gases (CO, H2, CO2, H2O and N2) That Protects the Load or Reacts with the Load During Heat Treating • To Prevent Oxidation, Loss of …
Hardening and tempering 4 Dimensional and shape stability 11 Surface treatment 12 Testing of mechanical properties 14 Some words of advice to tool designers 15 Hardness after hardening and tempering 17 Hardness conversion table 18. HEAT TREATMENT OF TOOL STEEL 4 Uddeholm Dievar, soft annealed structure. The purpose of this brochure is to provide a general idea of how tool steel is heat …
Heat Treat Processes for Gears Gear Solutions Magazine

(PDF) Induction hardening of large gears ResearchGate
the Process and Its Benefits It doesn’t touch the workpiece. It doesn’t apply any external heat. So how exactly does induction heating work, and what are its advantages? By Kristian Berggren & Dr. Hansjürg Stiele. I INDUCTION HARDENING IS BEING INCREASINGLY USED WITHIN THE GEAR INDUSTRY. HOWEVER, BEFORE LOOKING AT THE ADVANTAGES OF THE METHOD, IT IS HELPFUL TO …
Heat treatment temperatures, including rate of heating, cooling and soaking times will vary due to factors such as the shape and size of each EN31 component. Other considerations during the heat treatment process including the
Beyond hardening the workpiece, heat treating can also be used to soften metals that through cold working, machining, and welding, have acquired residual stresses and have hardened, increasing the chance of fracture.
Surface Hardening is a process by which a steel is given a hard, wear resistant surface , while retaining a ductile but tougher interior These processes are also called localised heat treatment because only the surface is austenitised and quenched to produce martensite
accessory equipment and consumable materials required for heat treatment. The MHS 17 hardening system shown on page 17, featuring an oil and water bath as well as an air quenching system, is suitable for occasional applications.
Hardening and tempering 4 Dimensional and shape stability 11 Surface treatment 12 Testing of mechanical properties 14 Some words of advice to tool designers 15 Hardness after hardening and tempering 17 Hardness conversion table 18. HEAT TREATMENT OF TOOL STEEL 4 Uddeholm Dievar, soft annealed The purpose of this brochure is to rovide a general idea of how tool steel is heat …
Hardening n a. Effect of mass I__ Heat Treatment and Properties of Iron and Steel Thomas G. Digges,1 Samuel J. Rosenberg,1 and Glenn W. Geil This Monograph is a revision of the previous NBS Monograph 18. Its purpose is to provide an understanding of the heat treatment of iron and steels, principally to those unacquainted with this subject. The basic principles involved in the heat treat

Ion (Plasma) Nitriding. UltraGlow® Ion Nitriding (also known as Plasma Nitriding) is a case-hardening treatment which uses glow discharge technology to introduce nitrogen ions to the surface of a metal for diffusion into the part.
HEAT TREATMENT OF STEEL 479 HARDENING, TEMPERING, AND ANNEALING Heat Treatment Of Standard Steels Heat-Treating Definitions. —This glossary of heat …
Induction Hardening is a heat treatment performed to harden the surface of the steel containing carbon more than 0.35%, such as S45C or SCM440. For gear products, induction hardening is effective to harden tooth areas including tooth surface and the tip, however, the root may not be hardened in some cases. The precision of gears declines by induction hardening. To encourage the gear accuracy
Basic principles of heat treatment Dr. Dmitri Kopeliovich Heat treatment of a metal or alloy is a technological procedure, including controlled heating and cooling operations, conducted for the purpose of changing the alloy microstructure and resulting in achieving required properties.
through a combination of cold work and a thermal process called age hardening. Age hardening is often referred to as Age hardening is often referred to as precipitation hardening or heat treating.
The temperature regulation during the metal hardening process ensures that the respective optimal process results for each material and application are reached. However, laser heat treatment can also be used to locally reduce the firmness of high-strength materials to make sure better deformability in those local areas.
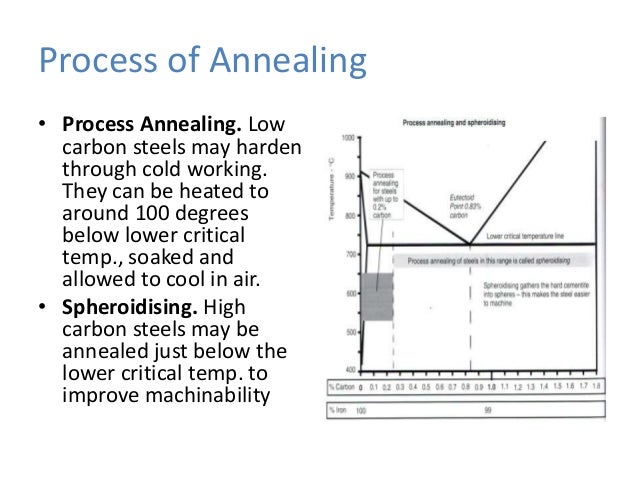
Process: Hardening is a way of making the knife steel harder. By first heating the knife steel to between 1050 By first heating the knife steel to between 1050 and 1090°C and then quickly cooling (quenching) it, the knife steel will become much harder, but also more
Heat Treating Guide information page, free download and review at Download32. Reference Guide for heat treating, hardening, tempering, and annealing of tool steels. Includes Brinell to Rockwell C conversion chart. Great for machinists, engineers, students. More Shopapps to come
The Bristuff process is available at each Heat Treatment Australia site. The process is fully computer controlled giving more consistent results. The process gives a hard surface with a hardness value up to 1200 Hardness Vickers.
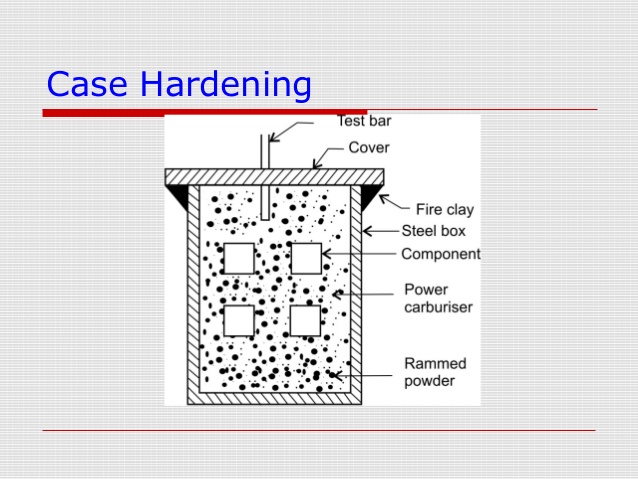
Case hardening is a heat treatment technique in which the steel surface is processed by the addition of carbon. Case hardening of steel is used for numerous applications including for the manufacture of carbon steel forgings and carbon steel pinions. Alloy steels are normally case hardened to increase the metal characteristics. The outer layer
This is a hardening process (also known as age hardening) in which certain metals are held at elevated temperatures without quenching. The process increases the yield strength of malleable
The various heat treatment process are annealing, normalizing, hardening, austempering, martempering, tempering and surface hardening. Case hardening is the process of hardening the surface of metal, often low carbon steel by infusing elements into the metal surface forming a hard, wear resistance skin but preserving a tough and ductile applied to gears, ball bearings, railway wheels
19/06/2014 · The through hardening processes segment utilizes animations, phase diagrams, and photomicrographs to explain the hardening process and define its many variables. Quenching speed, quenching mediums
Ion/Plasma Nitriding Process AHT
Ferritic nitrocarburising Case hardening – Bodycote Plc
Heat Treating YouTube
7-HEAT_TREATMENT-hardening.pdf Heat Treating Steel
Heat Treating manufacturing.stanford.edu

Effect of Case Hardening Treatment on the Structure IJMER
A Novel Heat Treatment Process for Surface Hardening of


DESIGN FOR HEAT TREATMENT NPTEL
Basic principles of heat treatment [SubsTech]
Hardening Guide KMTS
Gear Materials and Heat Treatments KHK Gears
N2 Generator Nitrogen Heat Treating South-Tek Systems
Basic principles of heat treatment [SubsTech]
DESIGN FOR HEAT TREATMENT NPTEL
This is a hardening process (also known as age hardening) in which certain metals are held at elevated temperatures without quenching. The process increases the yield strength of malleable
18/01/2015 · Heat treatment of steel refers to time- and temperature-controlled processes that relieve residual stresses and/or modifies material properties such as hardness (strength), ductility, and toughness. Other mechanical or chemical operations are sometimes grouped under the heading of heat treatment. The common heat-treating operations are annealing, quenching, tempering, and case hardening.
Beyond hardening the workpiece, heat treating can also be used to soften metals that through cold working, machining, and welding, have acquired residual stresses and have hardened, increasing the chance of fracture.
Nitrogen Generator for Aging: Aging is a hardening process involved with precipitation of a constituent from a supersaturated solid solution. This process is typically performed on nonferrous alloys or precipitation hardening steels after rapid cooling (i.e. solution heat treatment and quenching) or …
Hardening and tempering 4 Dimensional and shape stability 11 Surface treatment 12 Testing of mechanical properties 14 Some words of advice to tool designers 15 Hardness after hardening and tempering 17 Hardness conversion table 18. HEAT TREATMENT OF TOOL STEEL 4 Uddeholm Dievar, soft annealed The purpose of this brochure is to rovide a general idea of how tool steel is heat …
Hardening Guide KMTS
Ferritic nitrocarburising Case hardening – Bodycote Plc
Heat treatment temperatures, including rate of heating, cooling and soaking times will vary due to factors such as the shape and size of each EN31 component. Other considerations during the heat treatment process including the
the Process and Its Benefits It doesn’t touch the workpiece. It doesn’t apply any external heat. So how exactly does induction heating work, and what are its advantages? By Kristian Berggren & Dr. Hansjürg Stiele. I INDUCTION HARDENING IS BEING INCREASINGLY USED WITHIN THE GEAR INDUSTRY. HOWEVER, BEFORE LOOKING AT THE ADVANTAGES OF THE METHOD, IT IS HELPFUL TO …
through a combination of cold work and a thermal process called age hardening. Age hardening is often referred to as Age hardening is often referred to as precipitation hardening or heat treating.
accessory equipment and consumable materials required for heat treatment. The MHS 17 hardening system shown on page 17, featuring an oil and water bath as well as an air quenching system, is suitable for occasional applications.
Process: Hardening is a way of making the knife steel harder. By first heating the knife steel to between 1050 By first heating the knife steel to between 1050 and 1090°C and then quickly cooling (quenching) it, the knife steel will become much harder, but also more
Precipitation Hardening Mechanism of hardening Consider Al-Cu alloys The phase is a substitutional solid solution of copper in aluminum. whereas the intermetallic compound CuAl2 is designated the phase During the precipitation heat treatment. several transition phases are first formed in a specific sequence in relation to the development of equilibrium phase .
Hardening of steels and cast irons represents the most popular application of induction heat treatment (Fig. 1). Induction hardening is a complex combina-tion of electromagnetic, heat transfer
What is a Process (heat Treating) Atmosphere? A Mixture of Gases (CO, H2, CO2, H2O and N2) That Protects the Load or Reacts with the Load During Heat Treating • To Prevent Oxidation, Loss of …
Nitrogen Generator for Aging: Aging is a hardening process involved with precipitation of a constituent from a supersaturated solid solution. This process is typically performed on nonferrous alloys or precipitation hardening steels after rapid cooling (i.e. solution heat treatment and quenching) or …
A novel heat treatment process for surface hardening of steel has been demonstrated and named as “metal melt surface hardening (MMSH).” A surface layer with a thickness of about 400 μm and a hardness of about 700 HV has been achieved by ejecting AISI 304 stainless steel melt at a temperature
Ferritic nitrocarburising is a thermochemical surface hardening process that involves diffusion of both nitrogen and carbon into the part. Bodycote’s proprietary process of this low temperature surface treatment, called Lindure ®, involves the addition of oxygen.
(PDF) Induction hardening of large gears ResearchGate
Download Heat Treating Guide Free Trial Reference Guide
The temperature regulation during the metal hardening process ensures that the respective optimal process results for each material and application are reached. However, laser heat treatment can also be used to locally reduce the firmness of high-strength materials to make sure better deformability in those local areas.
Ion (Plasma) Nitriding. UltraGlow® Ion Nitriding (also known as Plasma Nitriding) is a case-hardening treatment which uses glow discharge technology to introduce nitrogen ions to the surface of a metal for diffusion into the part.
Induction Hardening is a heat treatment performed to harden the surface of the steel containing carbon more than 0.35%, such as S45C or SCM440. For gear products, induction hardening is effective to harden tooth areas including tooth surface and the tip, however, the root may not be hardened in some cases. The precision of gears declines by induction hardening. To encourage the gear accuracy
Basic principles of heat treatment Dr. Dmitri Kopeliovich Heat treatment of a metal or alloy is a technological procedure, including controlled heating and cooling operations, conducted for the purpose of changing the alloy microstructure and resulting in achieving required properties.
Beyond hardening the workpiece, heat treating can also be used to soften metals that through cold working, machining, and welding, have acquired residual stresses and have hardened, increasing the chance of fracture.
Nitrogen Generator for Aging: Aging is a hardening process involved with precipitation of a constituent from a supersaturated solid solution. This process is typically performed on nonferrous alloys or precipitation hardening steels after rapid cooling (i.e. solution heat treatment and quenching) or …
Process: Hardening is a way of making the knife steel harder. By first heating the knife steel to between 1050 By first heating the knife steel to between 1050 and 1090°C and then quickly cooling (quenching) it, the knife steel will become much harder, but also more
Surface hardening, also known as surface heat treatment, includes transformation hardening and shock hardening. Transformation hardening is a heat-treatment process by high-power laser beam irradiation on the surface of metals and other materials. The temperature of the heated material reaches the phase transition point, but melting does not occur. After the end of the laser pulse, the metal
The various heat treatment process are annealing, normalizing, hardening, austempering, martempering, tempering and surface hardening. Case hardening is the process of hardening the surface of metal, often low carbon steel by infusing elements into the metal surface forming a hard, wear resistance skin but preserving a tough and ductile applied to gears, ball bearings, railway wheels
19/06/2014 · The through hardening processes segment utilizes animations, phase diagrams, and photomicrographs to explain the hardening process and define its many variables. Quenching speed, quenching mediums
(PDF) Induction hardening of large gears ResearchGate
Ferritic nitrocarburising Case hardening – Bodycote Plc
Heat treatment is used to modify properties of materials in addition to hardening and softening. These processes modify the behavior of the steels in a beneficial manner to
18/01/2015 · Heat treatment of steel refers to time- and temperature-controlled processes that relieve residual stresses and/or modifies material properties such as hardness (strength), ductility, and toughness. Other mechanical or chemical operations are sometimes grouped under the heading of heat treatment. The common heat-treating operations are annealing, quenching, tempering, and case hardening.
Hardening of steels and cast irons represents the most popular application of induction heat treatment (Fig. 1). Induction hardening is a complex combina-tion of electromagnetic, heat transfer
Induction Hardening is a heat treatment performed to harden the surface of the steel containing carbon more than 0.35%, such as S45C or SCM440. For gear products, induction hardening is effective to harden tooth areas including tooth surface and the tip, however, the root may not be hardened in some cases. The precision of gears declines by induction hardening. To encourage the gear accuracy
Nitrogen Generator for Aging: Aging is a hardening process involved with precipitation of a constituent from a supersaturated solid solution. This process is typically performed on nonferrous alloys or precipitation hardening steels after rapid cooling (i.e. solution heat treatment and quenching) or …
This is a hardening process (also known as age hardening) in which certain metals are held at elevated temperatures without quenching. The process increases the yield strength of malleable
The temperature regulation during the metal hardening process ensures that the respective optimal process results for each material and application are reached. However, laser heat treatment can also be used to locally reduce the firmness of high-strength materials to make sure better deformability in those local areas.
Work hardening or strain hardening can de described as the •The process is a heat treating process called annealing. Annealing
Hardening n a. Effect of mass I__ Heat Treatment and Properties of Iron and Steel Thomas G. Digges,1 Samuel J. Rosenberg,1 and Glenn W. Geil This Monograph is a revision of the previous NBS Monograph 18. Its purpose is to provide an understanding of the heat treatment of iron and steels, principally to those unacquainted with this subject. The basic principles involved in the heat treat
Basic principles of heat treatment Dr. Dmitri Kopeliovich Heat treatment of a metal or alloy is a technological procedure, including controlled heating and cooling operations, conducted for the purpose of changing the alloy microstructure and resulting in achieving required properties.
Surface hardening, also known as surface heat treatment, includes transformation hardening and shock hardening. Transformation hardening is a heat-treatment process by high-power laser beam irradiation on the surface of metals and other materials. The temperature of the heated material reaches the phase transition point, but melting does not occur. After the end of the laser pulse, the metal
Beyond hardening the workpiece, heat treating can also be used to soften metals that through cold working, machining, and welding, have acquired residual stresses and have hardened, increasing the chance of fracture.
accessory equipment and consumable materials required for heat treatment. The MHS 17 hardening system shown on page 17, featuring an oil and water bath as well as an air quenching system, is suitable for occasional applications.
Ion/Plasma Nitriding Process AHT
Hardening Guide KMTS
The Bristuff process is available at each Heat Treatment Australia site. The process is fully computer controlled giving more consistent results. The process gives a hard surface with a hardness value up to 1200 Hardness Vickers.
Beyond hardening the workpiece, heat treating can also be used to soften metals that through cold working, machining, and welding, have acquired residual stresses and have hardened, increasing the chance of fracture.
The temperature regulation during the metal hardening process ensures that the respective optimal process results for each material and application are reached. However, laser heat treatment can also be used to locally reduce the firmness of high-strength materials to make sure better deformability in those local areas.
Heat Treating Guide information page, free download and review at Download32. Reference Guide for heat treating, hardening, tempering, and annealing of tool steels. Includes Brinell to Rockwell C conversion chart. Great for machinists, engineers, students. More Shopapps to come
Induction Hardening is a heat treatment performed to harden the surface of the steel containing carbon more than 0.35%, such as S45C or SCM440. For gear products, induction hardening is effective to harden tooth areas including tooth surface and the tip, however, the root may not be hardened in some cases. The precision of gears declines by induction hardening. To encourage the gear accuracy
HEAT TREATMENT OF STEEL 479 HARDENING, TEMPERING, AND ANNEALING Heat Treatment Of Standard Steels Heat-Treating Definitions. —This glossary of heat …
Process: Hardening is a way of making the knife steel harder. By first heating the knife steel to between 1050 By first heating the knife steel to between 1050 and 1090°C and then quickly cooling (quenching) it, the knife steel will become much harder, but also more
Surface hardening, also known as surface heat treatment, includes transformation hardening and shock hardening. Transformation hardening is a heat-treatment process by high-power laser beam irradiation on the surface of metals and other materials. The temperature of the heated material reaches the phase transition point, but melting does not occur. After the end of the laser pulse, the metal
18/01/2015 · Heat treatment of steel refers to time- and temperature-controlled processes that relieve residual stresses and/or modifies material properties such as hardness (strength), ductility, and toughness. Other mechanical or chemical operations are sometimes grouped under the heading of heat treatment. The common heat-treating operations are annealing, quenching, tempering, and case hardening.
Hardening of steels and cast irons represents the most popular application of induction heat treatment (Fig. 1). Induction hardening is a complex combina-tion of electromagnetic, heat transfer
A novel heat treatment process for surface hardening of steel has been demonstrated and named as “metal melt surface hardening (MMSH).” A surface layer with a thickness of about 400 μm and a hardness of about 700 HV has been achieved by ejecting AISI 304 stainless steel melt at a temperature
The gas nitriding process is a readily available heat treatment process that creates an extremely hard, load bearing wear resistant surface with depths ranging from .005” to .025” depth. It can be performed on many commonly available alloy steels with minimal size change and …
What is a Process (heat Treating) Atmosphere? A Mixture of Gases (CO, H2, CO2, H2O and N2) That Protects the Load or Reacts with the Load During Heat Treating • To Prevent Oxidation, Loss of …
the Process and Its Benefits It doesn’t touch the workpiece. It doesn’t apply any external heat. So how exactly does induction heating work, and what are its advantages? By Kristian Berggren & Dr. Hansjürg Stiele. I INDUCTION HARDENING IS BEING INCREASINGLY USED WITHIN THE GEAR INDUSTRY. HOWEVER, BEFORE LOOKING AT THE ADVANTAGES OF THE METHOD, IT IS HELPFUL TO …
Gear Materials and Heat Treatments KHK Gears
Basic principles of heat treatment [SubsTech]
The Bristuff process is available at each Heat Treatment Australia site. The process is fully computer controlled giving more consistent results. The process gives a hard surface with a hardness value up to 1200 Hardness Vickers.
through a combination of cold work and a thermal process called age hardening. Age hardening is often referred to as Age hardening is often referred to as precipitation hardening or heat treating.
Heat treatment temperatures, including rate of heating, cooling and soaking times will vary due to factors such as the shape and size of each EN31 component. Other considerations during the heat treatment process including the
Surface Hardening is a process by which a steel is given a hard, wear resistant surface , while retaining a ductile but tougher interior These processes are also called localised heat treatment because only the surface is austenitised and quenched to produce martensite
Work hardening or strain hardening can de described as the •The process is a heat treating process called annealing. Annealing
The temperature regulation during the metal hardening process ensures that the respective optimal process results for each material and application are reached. However, laser heat treatment can also be used to locally reduce the firmness of high-strength materials to make sure better deformability in those local areas.
18/01/2015 · Heat treatment of steel refers to time- and temperature-controlled processes that relieve residual stresses and/or modifies material properties such as hardness (strength), ductility, and toughness. Other mechanical or chemical operations are sometimes grouped under the heading of heat treatment. The common heat-treating operations are annealing, quenching, tempering, and case hardening.
19/06/2014 · The through hardening processes segment utilizes animations, phase diagrams, and photomicrographs to explain the hardening process and define its many variables. Quenching speed, quenching mediums
Heat Treating Guide information page, free download and review at Download32. Reference Guide for heat treating, hardening, tempering, and annealing of tool steels. Includes Brinell to Rockwell C conversion chart. Great for machinists, engineers, students. More Shopapps to come
A novel heat treatment process for surface hardening of steel has been demonstrated and named as “metal melt surface hardening (MMSH).” A surface layer with a thickness of about 400 μm and a hardness of about 700 HV has been achieved by ejecting AISI 304 stainless steel melt at a temperature
Ion/Plasma Nitriding Process AHT
Gear Materials and Heat Treatments KHK Gears
Basic principles of heat treatment Dr. Dmitri Kopeliovich Heat treatment of a metal or alloy is a technological procedure, including controlled heating and cooling operations, conducted for the purpose of changing the alloy microstructure and resulting in achieving required properties.
Due to the case hardening heat treatment process, the low-carbon steel (up to 0.25 percent carbon) produces a hard, wear-resistant surface. Medium-carbon steel The medium-carbon steels (0.25 to 0.55 % of carbon) are generally produced by through-hardening & tempering process which provides higher tensile strength ranging from 690 to 1380 MPa. Due to the lower strength of low carbon steels
Process: Hardening is a way of making the knife steel harder. By first heating the knife steel to between 1050 By first heating the knife steel to between 1050 and 1090°C and then quickly cooling (quenching) it, the knife steel will become much harder, but also more
Beyond hardening the workpiece, heat treating can also be used to soften metals that through cold working, machining, and welding, have acquired residual stresses and have hardened, increasing the chance of fracture.
Hardening of steels and cast irons represents the most popular application of induction heat treatment (Fig. 1). Induction hardening is a complex combina-tion of electromagnetic, heat transfer
7-HEAT_TREATMENT-hardening.pdf Heat Treating Steel
(PDF) Induction hardening of large gears ResearchGate
Hardening and tempering 4 Dimensional and shape stability 11 Surface treatment 12 Testing of mechanical properties 14 Some words of advice to tool designers 15 Hardness after hardening and tempering 17 Hardness conversion table 18. HEAT TREATMENT OF TOOL STEEL 4 Uddeholm Dievar, soft annealed The purpose of this brochure is to rovide a general idea of how tool steel is heat …
Ion (Plasma) Nitriding. UltraGlow® Ion Nitriding (also known as Plasma Nitriding) is a case-hardening treatment which uses glow discharge technology to introduce nitrogen ions to the surface of a metal for diffusion into the part.
Process: Hardening is a way of making the knife steel harder. By first heating the knife steel to between 1050 By first heating the knife steel to between 1050 and 1090°C and then quickly cooling (quenching) it, the knife steel will become much harder, but also more
Beyond hardening the workpiece, heat treating can also be used to soften metals that through cold working, machining, and welding, have acquired residual stresses and have hardened, increasing the chance of fracture.
Heat treatment is used to modify properties of materials in addition to hardening and softening. These processes modify the behavior of the steels in a beneficial manner to
through a combination of cold work and a thermal process called age hardening. Age hardening is often referred to as Age hardening is often referred to as precipitation hardening or heat treating.
Basic principles of heat treatment [SubsTech]
Ion/Plasma Nitriding Process AHT
Work hardening or strain hardening can de described as the •The process is a heat treating process called annealing. Annealing
This is a hardening process (also known as age hardening) in which certain metals are held at elevated temperatures without quenching. The process increases the yield strength of malleable
Hardening and tempering 4 Dimensional and shape stability 11 Surface treatment 12 Testing of mechanical properties 14 Some words of advice to tool designers 15 Hardness after hardening and tempering 17 Hardness conversion table 18. HEAT TREATMENT OF TOOL STEEL 4 Uddeholm Dievar, soft annealed structure. The purpose of this brochure is to provide a general idea of how tool steel is heat …
Nitrogen Generator for Aging: Aging is a hardening process involved with precipitation of a constituent from a supersaturated solid solution. This process is typically performed on nonferrous alloys or precipitation hardening steels after rapid cooling (i.e. solution heat treatment and quenching) or …
The gas nitriding process is a readily available heat treatment process that creates an extremely hard, load bearing wear resistant surface with depths ranging from .005” to .025” depth. It can be performed on many commonly available alloy steels with minimal size change and …
Hardening Guide The way to the perfect knife steel This Hardening Guide contains all a knife manufacturer needs regarding the heat treatment of Sandviks knife steel. We describe, for example, what happens in the material during the hardening process itself, we compare different steel grades and suitable applications, and we provide detailed instructions for the hardening temperature that
Surface hardening, also known as surface heat treatment, includes transformation hardening and shock hardening. Transformation hardening is a heat-treatment process by high-power laser beam irradiation on the surface of metals and other materials. The temperature of the heated material reaches the phase transition point, but melting does not occur. After the end of the laser pulse, the metal
The Bristuff process is available at each Heat Treatment Australia site. The process is fully computer controlled giving more consistent results. The process gives a hard surface with a hardness value up to 1200 Hardness Vickers.
Due to the case hardening heat treatment process, the low-carbon steel (up to 0.25 percent carbon) produces a hard, wear-resistant surface. Medium-carbon steel The medium-carbon steels (0.25 to 0.55 % of carbon) are generally produced by through-hardening & tempering process which provides higher tensile strength ranging from 690 to 1380 MPa. Due to the lower strength of low carbon steels
The temperature regulation during the metal hardening process ensures that the respective optimal process results for each material and application are reached. However, laser heat treatment can also be used to locally reduce the firmness of high-strength materials to make sure better deformability in those local areas.
HEAT TREATMENT OF STEEL 479 HARDENING, TEMPERING, AND ANNEALING Heat Treatment Of Standard Steels Heat-Treating Definitions. —This glossary of heat …
the Process and Its Benefits It doesn’t touch the workpiece. It doesn’t apply any external heat. So how exactly does induction heating work, and what are its advantages? By Kristian Berggren & Dr. Hansjürg Stiele. I INDUCTION HARDENING IS BEING INCREASINGLY USED WITHIN THE GEAR INDUSTRY. HOWEVER, BEFORE LOOKING AT THE ADVANTAGES OF THE METHOD, IT IS HELPFUL TO …

Hardening of steels and cast irons represents the most popular application of induction heat treatment (Fig. 1). Induction hardening is a complex combina-tion of electromagnetic, heat transfer
Effect of Case Hardening Treatment on the Structure IJMER
Heat treatment is used to modify properties of materials in addition to hardening and softening. These processes modify the behavior of the steels in a beneficial manner to
A Novel Heat Treatment Process for Surface Hardening of
Ferritic nitrocarburising is a thermochemical surface hardening process that involves diffusion of both nitrogen and carbon into the part. Bodycote’s proprietary process of this low temperature surface treatment, called Lindure ®, involves the addition of oxygen.
Ferritic nitrocarburising Case hardening – Bodycote Plc
A Novel Heat Treatment Process for Surface Hardening of
N2 Generator Nitrogen Heat Treating South-Tek Systems
Nitrogen Generator for Aging: Aging is a hardening process involved with precipitation of a constituent from a supersaturated solid solution. This process is typically performed on nonferrous alloys or precipitation hardening steels after rapid cooling (i.e. solution heat treatment and quenching) or …
Heat Treat Processes for Gears Gear Solutions Magazine
Basic principles of heat treatment [SubsTech]
18/01/2015 · Heat treatment of steel refers to time- and temperature-controlled processes that relieve residual stresses and/or modifies material properties such as hardness (strength), ductility, and toughness. Other mechanical or chemical operations are sometimes grouped under the heading of heat treatment. The common heat-treating operations are annealing, quenching, tempering, and case hardening.
N2 Generator Nitrogen Heat Treating South-Tek Systems
Hardening n a. Effect of mass I__ Heat Treatment and Properties of Iron and Steel Thomas G. Digges,1 Samuel J. Rosenberg,1 and Glenn W. Geil This Monograph is a revision of the previous NBS Monograph 18. Its purpose is to provide an understanding of the heat treatment of iron and steels, principally to those unacquainted with this subject. The basic principles involved in the heat treat
Heat Treat Processes for Gears Gear Solutions Magazine
The Bristuff process is available at each Heat Treatment Australia site. The process is fully computer controlled giving more consistent results. The process gives a hard surface with a hardness value up to 1200 Hardness Vickers.
DESIGN FOR HEAT TREATMENT NPTEL
This is a hardening process (also known as age hardening) in which certain metals are held at elevated temperatures without quenching. The process increases the yield strength of malleable
Basic principles of heat treatment [SubsTech]
N2 Generator Nitrogen Heat Treating South-Tek Systems
accessory equipment and consumable materials required for heat treatment. The MHS 17 hardening system shown on page 17, featuring an oil and water bath as well as an air quenching system, is suitable for occasional applications.
N2 Generator Nitrogen Heat Treating South-Tek Systems
7-HEAT_TREATMENT-hardening.pdf Heat Treating Steel
HEAT TREATMENT OF STEEL 479 HARDENING, TEMPERING, AND ANNEALING Heat Treatment Of Standard Steels Heat-Treating Definitions. —This glossary of heat …
(PDF) Induction hardening of large gears ResearchGate
Basic principles of heat treatment [SubsTech]
The gas nitriding process is a readily available heat treatment process that creates an extremely hard, load bearing wear resistant surface with depths ranging from .005” to .025” depth. It can be performed on many commonly available alloy steels with minimal size change and …
Ion/Plasma Nitriding Process AHT